- Services
- Companion Animal Blood Bank
Companion Animal Blood Bank
The Gift of Life
Sometimes our beloved pets have emergencies and illnesses, presenting a critical need for blood products. The Animal Blood Bank within the Veterinary Medical Center ensures our hospital feline and canine patients have access to blood products at a moment's notice.
Veterinarians and veterinary students can learn more about our available blood products, protocols for their safe use, and emergency acquisition.
In this section

In this section
Hours & Appointment Scheduling
We currently have available slots to add donors to our list!
The Animal Blood Bank is housed at the Veterinary Medical Center. Donors visit the Medical Center by appointment and after blood is collected, blood components are stored in state-of-the-art freezers and refrigerators for our in-house patient needs. For our referral partner hospitals, we may be able to accommodate emergency needs. If you have a patient blood emergency, please contact:
Cristina Iazbik, DVM
Clinical Lab Technician - Blood Bank Supervisor
Animal Blood Bank
Phone: (614) 688-8460
Email: CVM-osuvet.BloodBank@osu.edu
Blood Bank Hours:
Monday to Friday: 8:00 am to 4:00 pm
For after-hour blood emergencies, please call
(614) 292-3551 evenings, weekends and holidays
The mission of The Ohio State University Veterinary Blood Bank is two-fold:
- to provide a humane source of veterinary blood products for our canine and feline patients; and
- to provide education to ensure that our blood products are used to the best benefit of the patient.
We obtain our blood products from donor dogs and cats. As the demand for blood products increases, we are always interested in outreach to the public to enroll additional qualified donors.
Blood components are used primarily to treat patients at The Ohio State University Veterinary Medical Center, but now we've expanded the service to distribute blood products to veterinarians countrywide in emergency cases, as available.
Service Highlights
The Animal Blood Bank within the Veterinary Medical Center provides blood products as needed for our hospital canine and feline patients. The blood bank service would not be possible without the generous support of our animal blood donors, their families, and our generious partners who enable us to provide great benefits to our cat and dog blood donors and their families.
Thanks to the support of our generous partners, the benefits listed below are available at no cost throughout the year to animals currently enrolled in our blood donor program.
Because the health of our donors and the quality of our products is our priority, each year all our donors undergo a routine physical exam and blood work, including:
- a complete blood count (CBC),
- chemistry profile,
- serological test for heartworm disease and tick borne diseases in dogs
We also provide:
- heartworm preventative
- flea and tick control products
- high-quality nutrition
Not much I can say, except that the service at OSU has always been outstanding. I've been coming there for years with my little fur babies. I recommend your service to everyone.
Blood Products
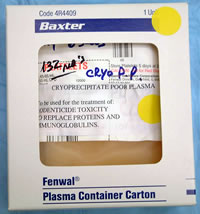
Cryoprecipitate-poor Plasma contains all coagulation factors except von Willebrand's factor and factor VIII. Therefore, it can be used in the treatment of rodenticide toxicity as well as the replacement of proteins (albumin and immunoglobulins). Cryopoor Plasma SHOULD NOT be used to treat von Willebrand's disease or Hemophilia A.
Protocol for use of Cryopoor Plasma
- Cryopoor Plasma should be thawed in a 37°C water bath in a waterproof plastic bag. Do not thaw in the refrigerator!
- Cryopoor Plasma must be administered with a standard in-line blood filter.
- The dose is 6-12 ml/kg, but in severe deficit of coagulation factors or immunoglobulin, you can use up to 20 ml/kg.
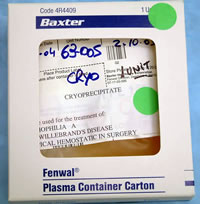
Cryoprecipitate is rich in factor VIII and von Willebrand's factor, so it is used for the treatment of hemophilia A and von Willebrand's disease; it can also be used as a topical hemostatic in surgery.
Protocol for use of cryoprecipitate
- Cryoprecipitate should be thawed in a 37°C water bath in a waterproof plastic bag. Do not thaw in the refrigerator!
- Cryoprecipitate must be administered with a standard in-line blood filter.
- The dose is 1 unit/10 kg.
- The dose can be repeated every 12 hours.

Protocol for use of fresh-frozen plasma
- Fresh-frozen plasma must be thawed in a 37°C water bath in a waterproof plastic bag. Do not thaw in the refrigerator or at room temperature!
- Fresh-frozen plasma should be administered immediately upon thawing.
- Fresh-frozen plasma must be administered through a standard blood or component administration set containing a 150-170µ filter.
- The dose is 10-15 ml/kg.
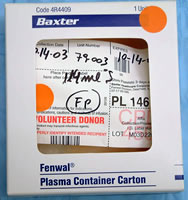
Frozen plasma contains minimal amounts of clotting factors V and VIII but can be used to treat rodenticide toxicity, hypoproteinemia, pancreatitis, antithrombin deficiency, or hemophilia B.
Protocol for use of frozen plasma
- Frozen plasma must be thawed in a 37°C water bath in a waterproof plastic bag. Do not thaw in the refrigerator or at room temperature!
- Frozen plasma should be administered immediately upon thawing.
- Frozen plasma must be administered through a standard blood or component administration set containing a 150-170µ filter.
- The dose is 10-15 ml/kg.
Used in patients with acute or chronic hemorrhage, hemolysis, renal disease, and bone marrow disorders.
Protocol for use of packed red Blood cells
- Packed red cells are preserved in an additive solution that does not require further dilution. However, if using fluids along with blood products, use normal saline.
- Avoid calcium-containing fluids such as Lactated Ringers or hypotonic fluids such as 5% dextrose in water.
- Use a standard blood administration set.
- Give 5ml/kg/hr for the first 15 min. then increase the rate.
- Dogs in cardiac, liver or renal failure should be given a dose of ∼1 ml/kg/hr.
- The transfusion must be completed within 4 hours to prevent the chance of bacterial growth.
- Transfusion of 15 ml/kg will raise the recipient's PCV by 10% points.
Program Sponsors
Thanks to each of the following companies for their generous support!